What Causes Urinary Tract Infection?
Overview
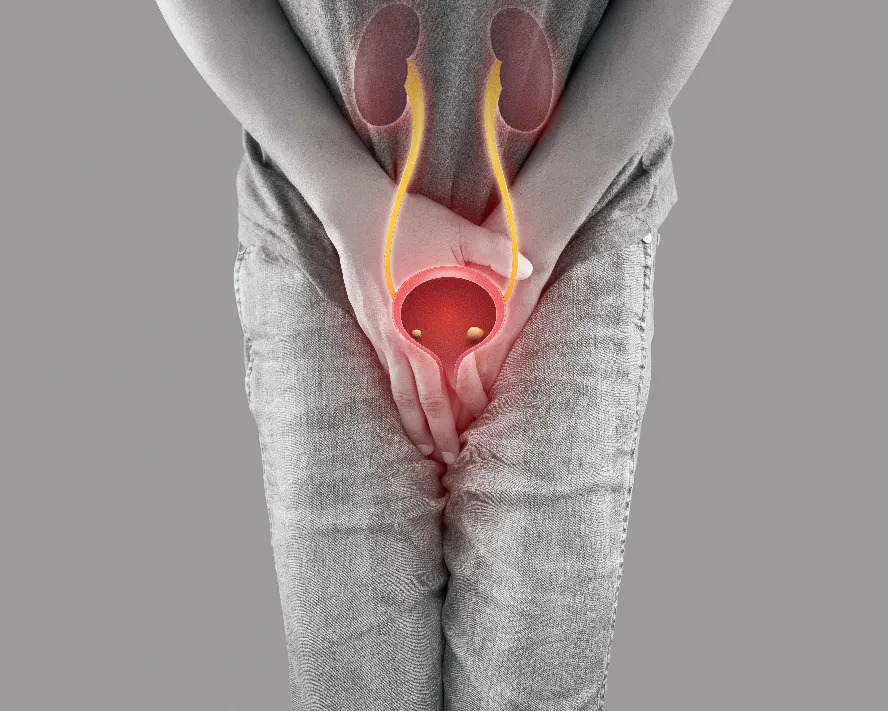
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections affecting individuals of all ages and sexes. They occur when pathogenic microorganisms, typically bacteria, invade and multiply within the urinary system.
The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Infections may involve any part of this system, but most commonly affect the bladder (cystitis) and the urethra (urethritis). More serious cases may ascend to the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis.
Common Causes of UTIs
1. Bacterial Entry Through the Urethra
The majority of UTIs are caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacterium normally found in the gastrointestinal tract. It can enter the urinary tract via the urethra, especially in women due to their shorter urethral length.
2. Sexual Activity
Sexual intercourse can facilitate the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract. This is sometimes referred to as “honeymoon cystitis” in women.
3. Incomplete Bladder Emptying
Urinary retention or incomplete voiding can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Common in individuals with prostate enlargement, neurogenic bladder, or after spinal cord injury.
4. Urinary Catheters
Indwelling catheters provide a direct pathway for bacteria to enter the bladder and are a significant risk factor for hospital-acquired UTIs.
5. Anatomical Abnormalities
Congenital abnormalities or acquired conditions like vesicoureteral reflux can predispose individuals, especially children, to recurrent infections.
6. Weakened Immune System
Conditions such as diabetes mellitus, immunosuppressive therapy, or aging can reduce the body’s defense mechanisms against infection.
7. Hormonal Changes
Postmenopausal women experience a drop in estrogen levels, leading to changes in the vaginal flora and increased susceptibility to UTIs.
Less Common Risk Factors
-
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis)
-
Recent urologic surgeries or procedures
-
Use of spermicides or diaphragms
-
Poor personal hygiene practices
Signs You Might Have a UTI
-
Burning sensation during urination
-
Frequent urge to urinate
-
Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
-
Lower abdominal discomfort
-
Fever or chills (in upper UTIs)
Prevention Strategies
-
Adequate hydration
-
Urinating after sexual activity
-
Avoiding unnecessary catheterization
-
Proper genital hygiene
-
Managing underlying conditions like diabetes
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are typically caused by bacterial colonization, but many modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors influence susceptibility. Recognizing and addressing these factors early can help in both prevention and effective management. Individuals with recurrent UTIs should undergo a comprehensive urological evaluation.

Social Media